Spiral Model
Spiral model is one of the most important Software Development Life Cycle models, which provides support for Risk Handling. In its diagrammatic representation, it looks like a spiral with many loops. The exact number of loops of the spiral is unknown and can vary from project to project. Each loop of the spiral is called a Phase of the software development process. The exact number of phases needed to develop the product can be varied by the project manager depending upon the project risks. As the project manager dynamically determines the number of phases, so the project manager has an important role to develop a product using the spiral model.
The Radius of the spiral at any point represents the expenses(cost) of the project so far, and the angular dimension represents the progress made so far in the current phase.
The below diagram shows the different phases of the Spiral Model: –
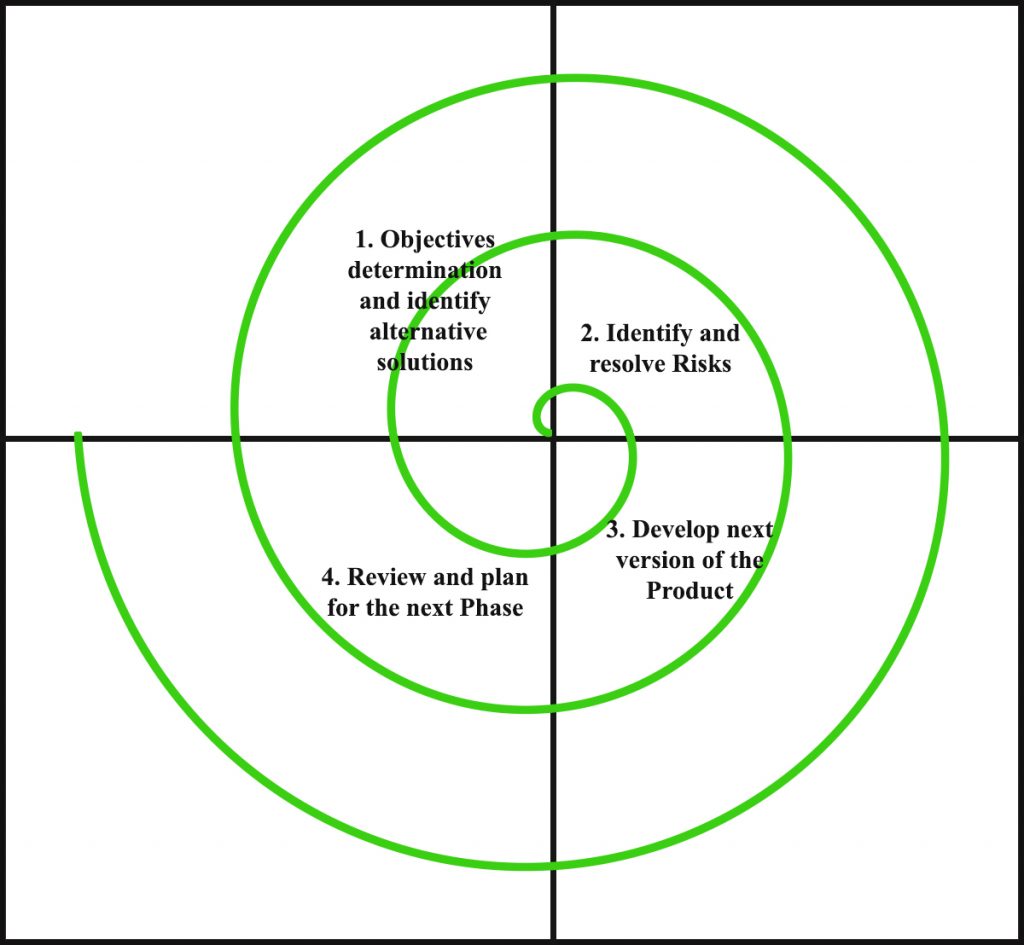
Each phase of the Spiral Model is divided into four quadrants as shown in the above figure. The functions of these four quadrants are discussed below-
- Objectives determination and identify alternative solutions: Requirements are gathered from the customers and the objectives are identified, elaborated, and analyzed at the start of every phase. Then alternative solutions possible for the phase are proposed in this quadrant.
- Identify and resolve Risks: During the second quadrant, all the possible solutions are evaluated to select the best possible solution. Then the risks associated with that solution are identified and the risks are resolved using the best possible strategy. At the end of this quadrant, the Prototype is built for the best possible solution.
- Develop next version of the Product: During the third quadrant, the identified features are developed and verified through testing. At the end of the third quadrant, the next version of the software is available.
- Review and plan for the next Phase: In the fourth quadrant, the Customers evaluate the so far developed version of the software. In the end, planning for the next phase is started.
Risk Handling in Spiral Model
A risk is any adverse situation that might affect the successful completion of a software project. The most important feature of the spiral model is handling these unknown risks after the project has started. Such risk resolutions are easier done by developing a prototype. The spiral model supports coping up with risks by providing the scope to build a prototype at every phase of the software development.
The Prototyping Model also supports risk handling, but the risks must be identified completely before the start of the development work of the project. But in real life project risk may occur after the development work starts, in that case, we cannot use the Prototyping Model. In each phase of the Spiral Model, the features of the product dated and analyzed, and the risks at that point in time are identified and are resolved through prototyping. Thus, this model is much more flexible compared to other SDLC models.
Why Spiral Model is called Meta Model?
The Spiral model is called a Meta-Model because it subsumes all the other SDLC models. For example, a single loop spiral actually represents the Iterative Waterfall Model. The spiral model incorporates the stepwise approach of the Classical Waterfall Model. The spiral model uses the approach of the Prototyping Model by building a prototype at the start of each phase as a risk-handling technique. Also, the spiral model can be considered as supporting the Evolutionary Model – the iterations along the spiral can be considered as evolutionary levels through which the complete system is built.
Advantages of Spiral Model:
Below are some advantages of the Spiral Model.
- Risk Handling: The projects with many unknown risks that occur as the development proceeds, in that case, Spiral Model is the best development model to follow due to the risk analysis and risk handling at every phase.
- Good for large projects: It is recommended to use the Spiral Model in large and complex projects.
- Flexibility in Requirements: Change requests in the Requirements at later phase can be incorporated accurately by using this model.
- Customer Satisfaction: Customer can see the development of the product at the early phase of the software development and thus, they habituated with the system by using it before completion of the total product.
Disadvantages of Spiral Model:
Below are some main disadvantages of the spiral model.
- Complex: The Spiral Model is much more complex than other SDLC models.
- Expensive: Spiral Model is not suitable for small projects as it is expensive.
- Too much dependability on Risk Analysis: The successful completion of the project is very much dependent on Risk Analysis. Without very highly experienced experts, it is going to be a failure to develop a project using this model.
- Difficulty in time management: As the number of phases is unknown at the start of the project, so time estimation is very difficult.