V-Model
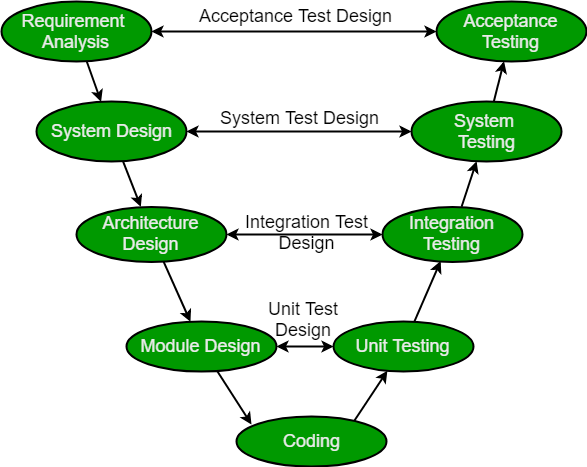
The V-model is a type of SDLC model where process executes in a sequential manner in V-shape. It is also known as Verification and Validation model. It is based on the association of a testing phase for each corresponding development stage. Development of each step directly associated with the testing phase. The next phase starts only after completion of the previous phase i.e. for each development activity, there is a testing activity corresponding to it.
Verification: It involves static analysis technique (review) done without executing code. It is the process of evaluation of the product development phase to find whether specified requirements meet.
Validation: It involves dynamic analysis technique (functional, non-functional), testing done by executing code. Validation is the process to evaluate the software after the completion of the development phase to determine whether software meets the customer expectations and requirements.
So V-Model contains Verification phases on one side of the Validation phases on the other side. Verification and Validation phases are joined by coding phase in V-shape. Thus it is called V-Model.
Design Phase:
- Requirement Analysis: This phase contains detailed communication with the customer to understand their requirements and expectations. This stage is known as Requirement Gathering.
- System Design: This phase contains the system design and the complete hardware and communication setup for developing product.
- Architectural Design: System design is broken down further into modules taking up different functionalities. The data transfer and communication between the internal modules and with the outside world (other systems) is clearly understood.
- Module Design: In this phase the system breaks down into small modules. The detailed design of modules is specified, also known as Low-Level Design (LLD).
Testing Phases:
- Unit Testing: Unit Test Plans are developed during module design phase. These Unit Test Plans are executed to eliminate bugs at code or unit level.
- Integration testing: After completion of unit testing Integration testing is performed. In integration testing, the modules are integrated and the system is tested. Integration testing is performed on the Architecture design phase. This test verifies the communication of modules among themselves.
- System Testing: System testing test the complete application with its functionality, inter dependency, and communication.It tests the functional and non-functional requirements of the developed application.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): UAT is performed in a user environment that resembles the production environment. UAT verifies that the delivered system meets user’s requirement and system is ready for use in real world.
Industrial Challenge: As the industry has evolved, the technologies have become more complex, increasingly faster, and forever changing, however, there remains a set of basic principles and concepts that are as applicable today as when IT was in its infancy.
- Accurately define and refine user requirements.
- Design and build an application according to the authorized user requirements.
- Validate that the application they had built adhered to the authorized business requirements.
Principles of V-Model:
- Large to Small: In V-Model, testing is done in a hierarchical perspective, For example, requirements identified by the project team, create High-Level Design, and Detailed Design phases of the project. As each of these phases is completed the requirements, they are defining become more and more refined and detailed.
- Data/Process Integrity: This principle states that the successful design of any project requires the incorporation and cohesion of both data and processes. Process elements must be identified at each and every requirements.
- Scalability: This principle states that the V-Model concept has the flexibility to accommodate any IT project irrespective of its size, complexity or duration.
- Cross Referencing: Direct correlation between requirements and corresponding testing activity is known as cross-referencing.
- Tangible Documentation: This principle states that every project needs to create a document. This documentation is required and applied by both the project development team and the support team. Documentation is used to maintaining the application once it is available in a production environment.
Why preferred?
- It is easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model. Each phase of V-Model has specific deliverables and a review process.
- Proactive defect tracking – that is defects are found at early stage.
When to use?
- Where requirements are clearly defined and fixed.
- The V-Model is used when ample technical resources are available with technical expertise.
Advantages:
- This is a highly disciplined model and Phases are completed one at a time.
- V-Model is used for small projects where project requirements are clear.
- Simple and easy to understand and use.
- This model focuses on verification and validation activities early in the life cycle thereby enhancing the probability of building an error-free and good quality product.
- It enables project management to track progress accurately.
Disadvantages:
- High risk and uncertainty.
- It is not a good for complex and object-oriented projects.
- It is not suitable for projects where requirements are not clear and contains high risk of changing.
- This model does not support iteration of phases.
- It does not easily handle concurrent events.